티스토리 뷰
멀티캠퍼스 AI과정/04 Pandas
Pandas 02 - DataFrame describe(), indexing, 행/칼럼 추가, 삭제
jhk828 2020. 9. 11. 03:17DataFrame에 대한 이야기
describe()
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = {'이름' : ['이지은', '박동훈', '홍길동', '강감찬', '오혜영'],
'학과': ['컴퓨터', '기계', '철학', '국어국문', '컴퓨터'],
'학년': [1, 2, 2, 4, 3],
'학점': [1.5, 2.0, 3.1, 1.1, 2.8]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data,
columns=['학과', '이름', '학점', '학년'],
index = ['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five'])
display(df)
# DataFRame 안에 있는 숫자연산이 가능한 column에 한해,
# 기본분석함수 적영한 수치값들을 DataFrame으로 리턴
display(df.describe())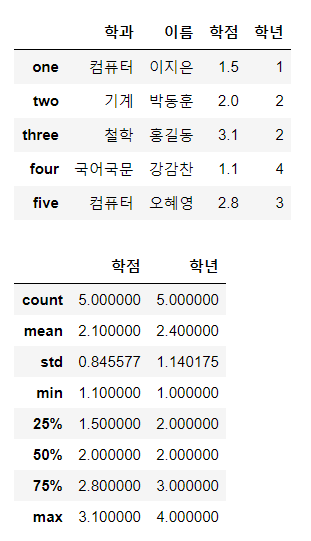
DataFrame의 indexing
Column을 추출하는 방법
- DataFrame에서는 특정 column을 추출할 수 있으며, 그 결과는 Series가 된다.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = {'이름' : ['이지은', '박동훈', '홍길동', '강감찬', '오혜영'],
'학과': ['컴퓨터', '기계', '철학', '국어국문', '컴퓨터'],
'학년': [1, 2, 2, 4, 3],
'학점': [1.5, 2.0, 3.1, 1.1, 2.8]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data,
columns=['학과', '이름', '학점', '학년', '등급'],
index=['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five'])
display(df)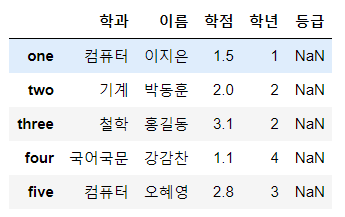
## column 추출하기
print(df['이름']) # 결과는 Series로 return
# print(df.이름) # 되기는 하지만, 프로그래밍에 적합한 형태x, 많이 사용x"
year = df['학년'] # year는 Series가 된다. => View!!
year['one'] = 100 # Series의 내용 변경
print(year)
display(df) # 원본도 변경
Column을 추출하는 방법 -> Fancy Indexing
- 두 개 이상의 column을 추출하면 DataFrame으로 리턴
display(df[['학과', '학점']])
# display(df['학과', '학점']) # Error
# display(df['학과' : '학점']) # Error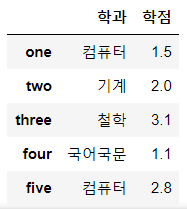
DataFrame에서 특정 column의 값 수정
- 단일값 (Scalar), list, numpy array를 이용해서 수정할 수 있다.
print("단일값으로 column 수정 -> Broadcasting")
df['등급'] = 'A' # Scalar 값을 넣었지만, Broadcasting이 일어남
display(df)
print("\nlist로 column 수정")
df['등급'] = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'F']
display(df)
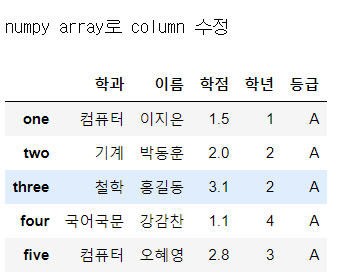
print("\nnumpy array로 column 수정")
df['등급'] = np.array(['A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A'])
display(df)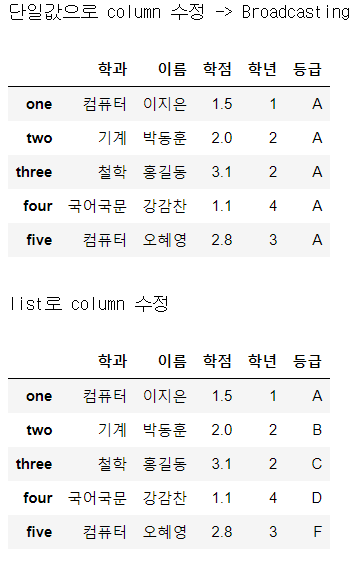
DataFrame에서 두개 이상의 특정 column 값 수정
- 단일값, list, numpy array,를 이용해서 수정할 수 있다.
df[['학과', '등급']] = 'A'
display(df)
df[['학과', '등급']] = [['영어영문', 'A'],
['철학', 'C'],
['수학', 'D'],
['기계', 'B'],
['영어영문', 'A'],]
display(df)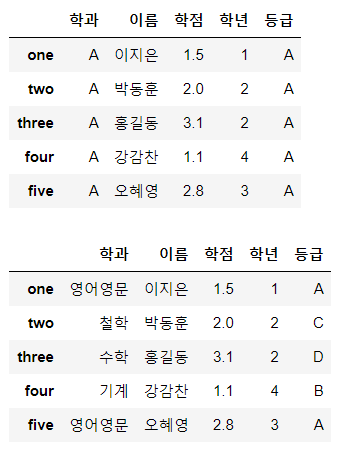
새로운 column을 DataFrame에 추가
- 단일값, list, numpy array를 이용해서 추가할 수 있다.
df['나이'] = [20, 21, 22, 23, 24] # column을 추가하려면 갯수가 맞아야 한다.
display(df)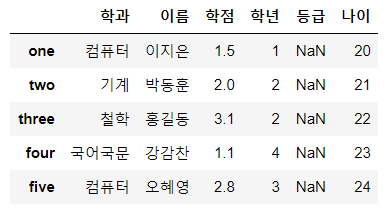
Series로 새로운 column을 추가할 때는 index를 매칭시켜야 한다.
- Series로 column을 추가할 때는 값의 대입 기준이 index이기 때문
# df['나이'] = pd.Series([20, 21, 22, 23, 24])
# display(df)
# 추가가 안된다.
# Series로 column을 추가할 때는 값의 대입 기준이 index이기 때문
df['나이'] = pd.Series([20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
index=['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five'])
display(df)
df['나이'] = pd.Series([20, 21, 22],
index=['one', 'two', 'three'])
display(df)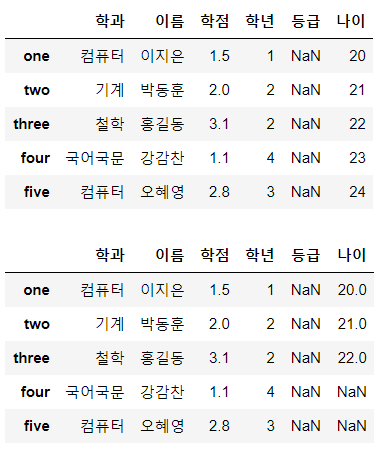
새로운 column을 column의 연산을 통해 추가할 수 있다
# 마지막에 column을 하나 추가한다. => '장학생 여부'
# 만약 학점이 3.0 이상이면 True, 그렇지 않으면 False
df['장학생여부'] = df['학점'] > 3.0
display(df)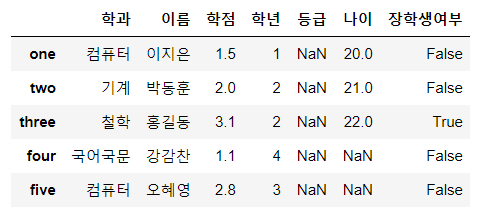
DataFrame에서 column을 삭제 => drop()
-
함수를 이용해서 column 삭제 가능
-
열(column)을 삭제할 경우, 행(row)를 삭제할 경우 둘 다
drop()사용 -
함수 사용 시 주의해야 할 점 : 행/ 열 어떤거 삭제할지 명시해야 한다.
-
inplace=True=> 원본을 지운다. return 존재x -
inplace=False=> 원본은 보존하고 삭제된 결과물 df를 만들어서 return -
default값은
inplace=False
new_df = df.drop('학년', axis=1, inplace=False)
display(new_df)
# Fancy Indexing으로 삭제
new_df = df.drop(['학점', '등급'], axis=1, inplace=False)
display(new_df)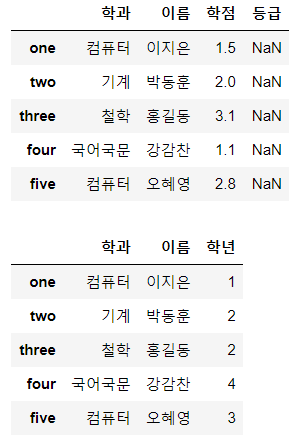
column/ row indexing
- row는 slicing은 되는데 단일인덱싱이 안됨
- column은 slicing은 안되는데 단일 인덱싱이 됨
1) column indexing
# 단일 column indexing
print(df['이름']) # OK. Series로 리턴
# display(df['학과':'학점']) # Error. column에 대해서 slicing은 지원x
display(df[['학과', '학점']]) # OK. column에 대해서 Fancy indexing은 가능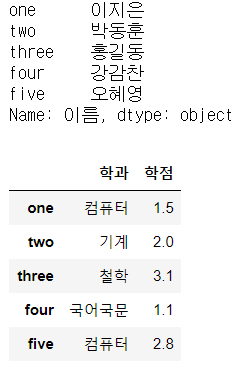
2-1) row indexing - part1: 숫자 인덱스
# print(df[0]) # Error. row에 대해서 숫자 index로 단일 indexing이 안된다.
display(df[1:3]) # 단일인덱싱은 안되는데 slicing이 된다.
display(df[1:])
# display(df[[0, 2]]) # Error. row에 대해 index 숫자를 이용한 fancy indexing은 지원x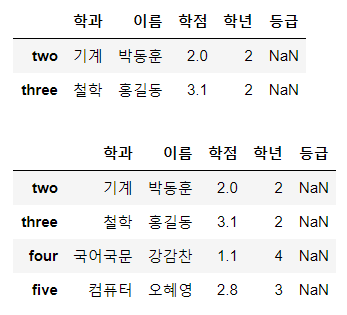
2-2) row indexing - part2: 행에 대한 별도의 index
# display(df['one']) # Error
display(df['one':'three']) # OK. one<= x <= three
# display(df['three':-1]) # Error. 숫자 index와 index를 혼용하여 사용할 수 X
# display(df[['two', 'four']]) # Error. Fancy indexing x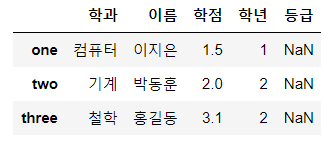
2-3) row indexing - part3 : loc[]를 row indexing
- 많이 사용하는 방법 중 하나
- loc를 이용할 때는 숫자 index가 아닌 부여한 index를 사용
print(df.loc['one']) # OK. loc와 index를 이용하면 단일 row 추출 가능.
# Series로 return
# print(df.loc[0]) # Error. loc는 숫자 index 사용 X
display(df.loc['one':'three']) # OK. slicing도 가능.
display(df.loc['three':])
# display(df.loc['one':-1]) # Error. index를 혼합해서 사용하는건 안된다.
display(df.loc[['one', 'three']]) # OK. fancy indexing도 가능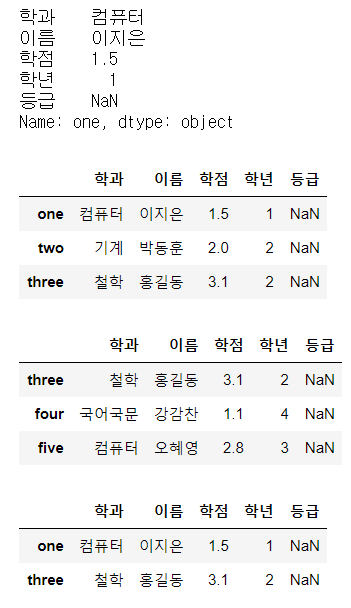
2-4) row indexing - part4 : iloc[]
loc[]와 다른 점은, 숫자만 사용할 수 있다.
loc[]를 이용하면, 행과 열을 동시에 추출할 수 있다.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = {'이름' : ['이지은', '박동훈', '홍길동', '강감찬', '오혜영'],
'학과': ['컴퓨터', '기계', '철학', '국어국문', '컴퓨터'],
'학년': [1, 2, 2, 4, 3],
'학점': [1.5, 2.0, 3.1, 1.1, 2.8]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data,
columns=['학과', '이름', '학점', '학년', '등급'],
index=['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five'])
display(df)
##########################
## 행 추출하기
display(df.loc['one':'three'])
# 행 뿐만 아니라 열도 같이 추출할 수 있다.
display(df.loc['one':'three', '이름']) # Series
# 행, 열 둘 다 slicing
display(df.loc['one':'three', '이름':'학년']) # Dataframe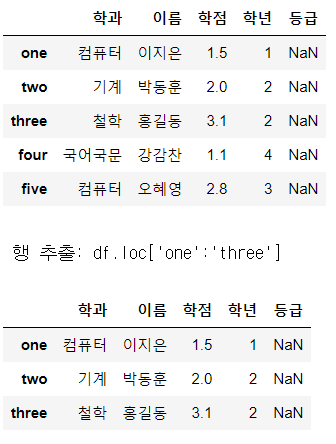

loc[]에 Boolean Mask로 행 추출
# 학점이 1.5점을 초과하는 학생의 이름과 학점 DataFrame으로 추출
# df['학점']>1.5 => Boolean Mask를 행 추출 시 사용
print(df['학점']>1.5)
display(df.loc[df['학점']>1.5,['이름','학점']]) 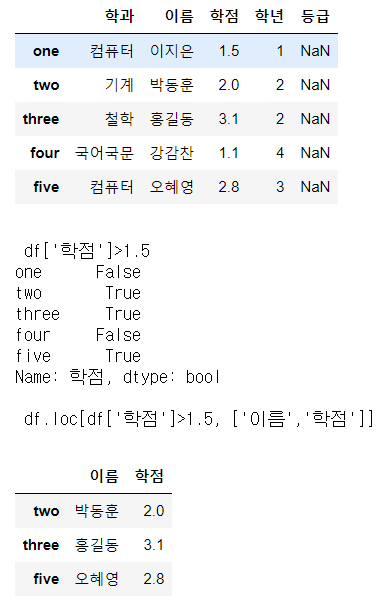
# 1. 이름이 '박동훈'인 사람을 찾아 이름과 학점을 DataFrame으로 출력
display(df.loc[df['이름']=='박동훈',['이름','학점']])
# 2. 학점이 1.5 초과 2.5 미만인 모든 사람을 찾아 학과, 이름, 학점을 DataFrame으로 출력
display(df.loc[(df['학점'] > 1.5) & (df['학점'] < 2.5),'학과':'학점'])
# 3. 학점이 3.0을 초과하는 사람을 찾아 등급을 'A'로 설정한 후 출력
df.loc[df['학점'] > 3.0, '등급'] = 'A'
display(df)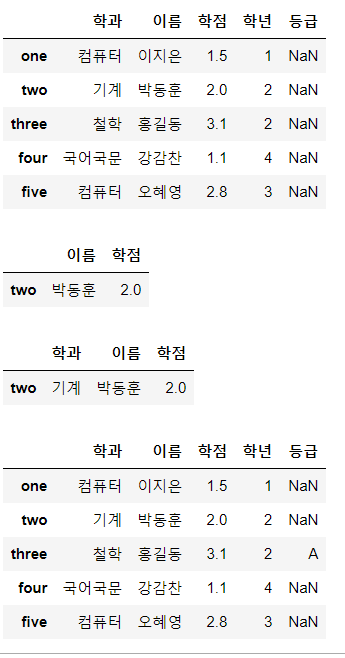
iloc[]를 이용하여 행과 열 indexing
- numpy에서는 행과 열에 동시에 fancy indexing이 안된다.
- numpy에서는
np.ix_()함수를 사용한다.
- numpy에서는
- DataFrame에서는
iloc[]를 이용한 행과 열 fancy indexing이 동시에 된다.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = { '이름': ['이지은', '박동훈', '홍길동', '강감찬', '오혜영'],
'학과':['컴퓨터','기계','철학','컴퓨터','철학'],
'학년':[1, 2, 2, 4, 3],
'학점':[1.5, 2.0, 3.1, 1.1, 2.7]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data,
columns = ['학과', '이름', '학점', '학년', '등급'],
index = ['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five'])
display(df)
############################################
print(df.iloc[0, 0]) # 컴퓨터
print(df.iloc[1]) # Series
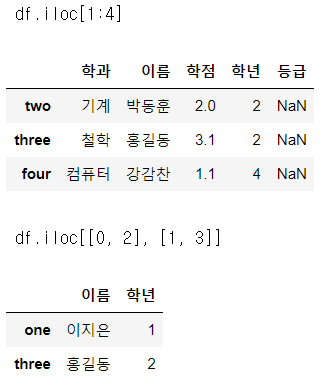
display(df.iloc[1:4])
# DataFrame에서는 iloc[]를 이용한 행과 열 fancy indexing이 동시에 된다.
display(df.iloc[[0, 2], [1, 3]])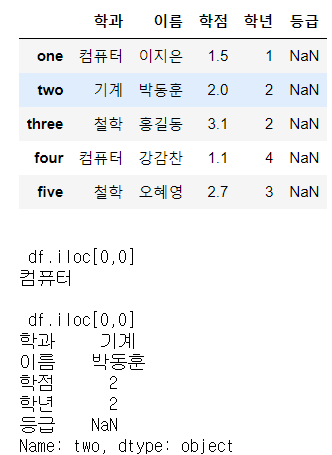
DataFrame에서 새로운 행을 추가
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = { '이름':['이지은','박동훈','홍길동','강감찬','오혜영'],
'학과':['컴퓨터','기계','철학','컴퓨터','철학'],
'학년':[1, 2, 2, 4, 3],
'학점':[1.5, 2.0, 3.1, 1.1, 2.7]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data,
columns=['학과','이름','학점','학년','등급'],
index=['one','two','three','four','five'])
display(df)
########################################
df.loc['six', :] = ['영어영문', '최길동', 4.0, 3, 'A']
display(df)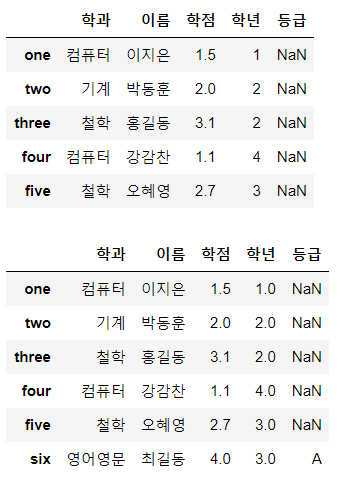
df.loc['six', ['학과', '이름']] = ['영어영문', '최길동']
display(df)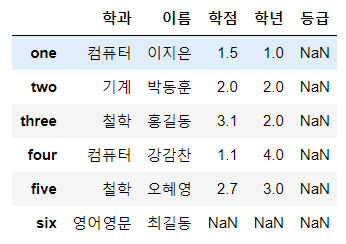
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = { '이름':['이지은','박동훈','홍길동','강감찬','오혜영'],
'학과':['컴퓨터','기계','철학','컴퓨터','철학'],
'학년':[1, 2, 2, 4, 3],
'학점':[1.5, 2.0, 3.1, 1.1, 2.7]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data,
columns=['학과','이름','학점','학년','등급'],
index=['one','two','three','four','five'])
display(df)
################################
# DataFrame에서 특정 컬럼 삭제
display(df.drop('학점', axis=1, inplace=False))
# DataFrame에서 특정 행 삭제
display(df.drop(['two','five'], axis=0, inplace=False))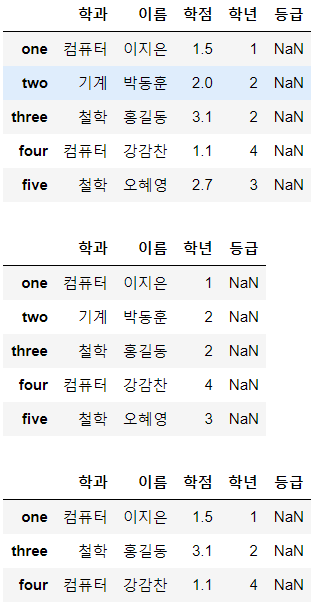
'멀티캠퍼스 AI과정 > 04 Pandas' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Pandas 04 - 결측치 처리 (0) | 2020.09.15 |
|---|---|
| Pandas 04 - DataFrame 결합 Mearge (Join) (0) | 2020.09.15 |
| Pandas 03 - DataFrame 집계함수, 통계기반 함수, 정렬, apply와 lambda (0) | 2020.09.15 |
| Pandas 02 - DataFrame (2차원) (0) | 2020.09.09 |
| Pandas 01 - Series (1차원) (0) | 2020.09.09 |
댓글
